Getting startedFunctionsVariablesVariables 2InputsSelectionFlowchartsData typesPseudocode1Pseudocode2Subprogram1Subprogram2 |
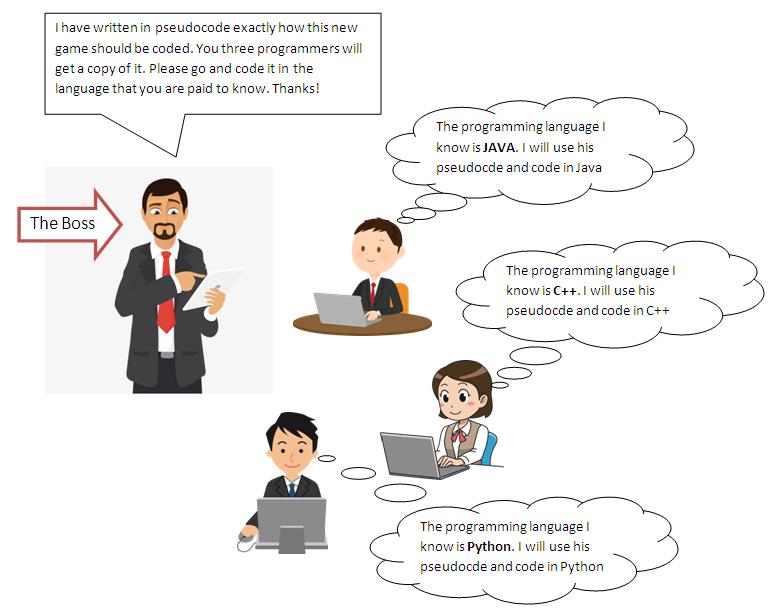
Pseudocode (pronounced "Sue-doe-code")Psedocode looks a lot like a programming language but it isn't, because computers don't understand it. It is because Humans understand pseudocode and computers do not, that makes pseudocode really useful. Professional programmers that make software, apps or playstation games normally know how to write code in just one of the hundreds of different programming languages. This means that if you have a team of programmers that all understand different programming languages and you want them all to make a new game, you can write the code in pseudocode and give them each a copy. They will be able to understand your pseudocode and then write code in the programming language they understand.
Pseudocode explainedHow much pseudocode is there?Below is a list of pseudocode constructs that have already been covered. Click here for a PDF version.
Variables
Selection
Input/Output
Subprograms
Test you knowledge
Loading Comparison operators
Loading Python pseudocode conversion
|