Edexcel curriculum (2015)
PythonBinary/HexData representationCompressionEncryptionWhat is a computer?Working computerHardwareOperating systemComputer processesThe CPUMemoryInput devicesOutput devicesData storageInside the CPUStored programF-D-E cycleCPU componentsNetworksLAN, WAN and PANNetwork topologiesNetwork addressingProtocolsError detectionThe internetThe world wide webHTML and CSSClient-server modelVPNsSQLImpactEthical issuesMicrocontrollersComp modelsEmerging trendsVirtual machines
Models and simsAlgorithms |
Computational modelsA sequential computational model is one in which instructions are executed one after another. There may be branches in the program, but the general principle is that each instruction follows on from the previous one.
Python programs are sequential. A parallel computational model is one in which each program instruction is executed simultaneously on multiple processors in order to get the results faster. Using multi-cores in processors is an example of parallel computing. It is by using parallel processing that super computers are getting faster and faster. Computational model - Multi-agent
Artificial intelligenceWhat comes to mind when you think about artificial intelligence (AI).?
Game playing: programming computers to play games against human opponents (in May 1997, an IBM super-computer called Deep Blue defeated world chess champion Gary Kasparov in a chess match) Expert systems: programming computers to make decisions in real-life decisions (e.g. disease diagnosis based on symptoms) Natural language: programming computers to understand human languages Neural networks: systems that simulate intelligence by attempting to reproduce connections in animal brains Robotics: programming computers to react to sensory stimuli.
Nanotechnology
In the future, nanotechnology could impact on all industries and all areas of society, including: communications, medicine, transportation and agriculture.
DNA ComputingDNA computing is a branch of computing which uses DNA, biochemistry, and molecular biology hardware, instead of the traditional silicon-based computer technologies.
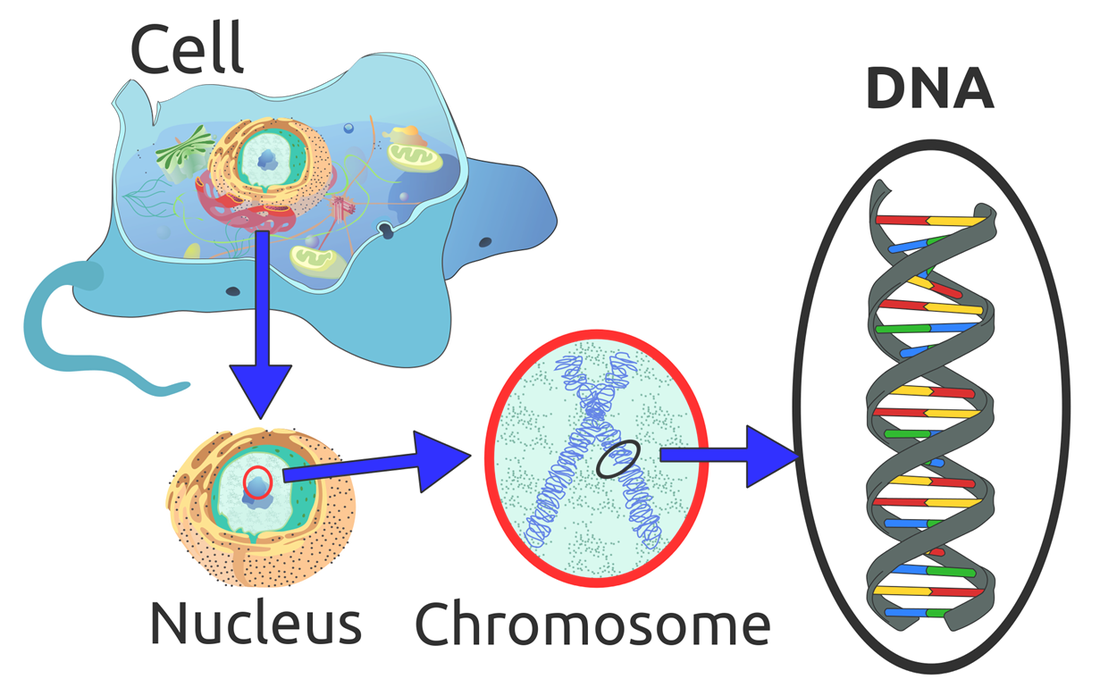
In every cell in your body there is a nucleus In every nucleus there is a chromosome A chromosome is made up of DNA DNA stores data. Your DNA stores data about you. We can manipulate DNA to store any data in the same way we use transistors to store information. Hence the term DNA computing
The main benefit of using DNA computers is that they can solve many complex problems at the same time. This known as: parallel processing. As it is possible to fit 100 trillion DNA molecules into an area less than 1cm3, a DNA computer could hold 100 tb of data and parallel process 10 trillion calculations at the same time. Quantum computingWhat is Moors law?
"Moore's law" is the observation that, over the history of computing hardware, the number of transistors in a dense integrated circuit has doubled approximately every two years. If Moors law is right, then there will be a time when we can no longer fit more transistors on a CPU we have to look at emerging fields such as quantum computing and DNA computing. Quantum computing Is based on quantum physics Conventional computers work by processing data stored as bits in one of two states: 1 or 0, Quantum computers encode data as quantum bits (or qubits) which means they are not limited to storing data in just two states. Individual qubits can represent a value of 1 or 0 or both numbers simultaneously. Past exam questionsBelow is a past paper question. Attempt it before viewing the answer. Goodluck!
|