1 Answer
- Input device: touch screen / microphone / accelerometer/(hardware) button/ camera / (hard) keyboard
- Output device: screen / speaker / vibrating device / LEDs
- Storage device: Solid state memory e.g. SD card, memory card, flash memory , SIM card
More help here - Input/Output/Storage devices
2A answer
2b answer
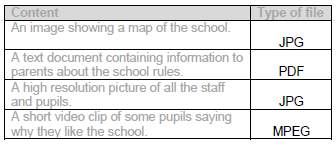
When the file is compressed some detail/data/quality/resolution is lost...
... which is not noticeable in the video file/video still viewable with lower quality
… but would make the text file unreadable/lose meaning or comprehension
More help here - Lossy vs lossless
... which is not noticeable in the video file/video still viewable with lower quality
… but would make the text file unreadable/lose meaning or comprehension
More help here - Lossy vs lossless
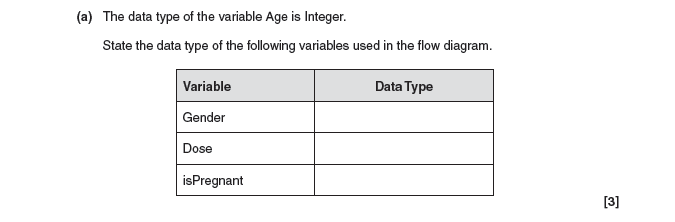
3a answer
3b answer
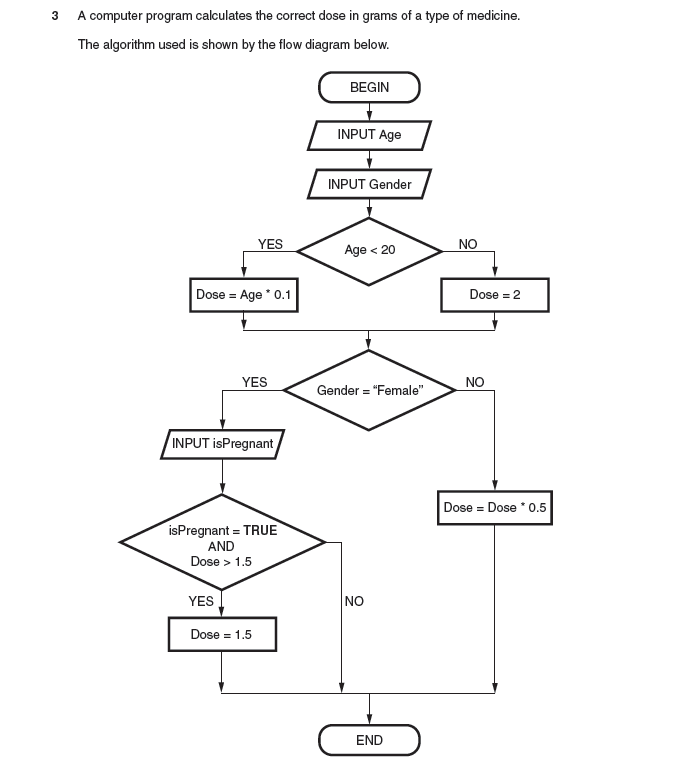
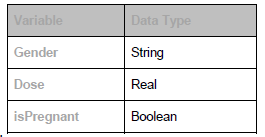
- (Age < 20 is FALSE so) Dose = 2
- ( Gender = “Female” is FALSE) so Dose = Dose * 0.5
- ... therefore Dose = 1
3c answer
- (Age is less than 20 = true) so Dose = 0.1 * Age
- 1.9
- [ isPregnant AND Dose > 1.5 ] is TRUE
- Dose = 1.5
4a answer
4b answer
e.g.
(User name and) password
Only allows you to use the system if you are authorised
Encryption
Prevents hackers from understanding any data if accessed (e.g. passwords)
Access rights
To prevent files from being modified/deleted
User access control
Prevents users from making changes to the system
Marks in pairs
More help here - OS security
(User name and) password
Only allows you to use the system if you are authorised
Encryption
Prevents hackers from understanding any data if accessed (e.g. passwords)
Access rights
To prevent files from being modified/deleted
User access control
Prevents users from making changes to the system
Marks in pairs
More help here - OS security
5ai answer
High level code :
More help here - HLL and machine code
- human oriented code / written by programmers
- contains words for commands / closer to English/natural language
- Machine independent /Portable to different systems
- Needs to be translated before it can be executed.
- Problem based
- One (high level) command equates to many machine code instructions.
- Code for the CPU to execute / not readily understandable by humans
- binary instructions
- specific to a particular (type of) computer / not portable to different systems
- does not need to be translated
More help here - HLL and machine code
5aii answer
- To translate the high level code into machine code
- To pick up (syntax) errors
More help here - Compiler
5b answer
Examples of standards;
- Code should be written using standard/agreed conventions
- ... such as in the choice/capitalisation of variable names
- …language chosen
- ..use of functions
- ..comments
- Meaningful identifiers
- Indenting (constructs)
- … compatibility between components
- ..consistency
- …allow multiple people to work on the same project
- …ensure coding conventions are kept
- …so others can read/edit the code
6a answer
Software that is produced for a variety of users / not for a specific user / commercially available to anyone / immediately available
More help here - Off the shelf
More help here - Off the shelf
6b answer
- Create tables / entities
- Define fields / attributes / columns
- Define (primary) keys
- Define relationships / links between tables / foreign keys
- Set the constraints on the data /validation rules / data types / field lengths / other suitable example
More help here - Database explained
6c answer
e.g.
More help here - Why use a databse
- Add client/appointment data
- Edit client/appointment data
- Delete client/appointment data
- Run/Create/View reports using a relevant example of a report that would be needed e.g. today’s appointments
- Search/query for data using a relevant e.g. search for a client’s phone number
- Back up (client/appointment) data.
- Archive (client/appointment) data/ example of archiving
More help here - Why use a databse
7a answer
- Instructions/programs(currently running)/data are stored in the RAM...
- these are fetched from the RAM by the CPU /Processor
- ... where the instructions are executed / instructions are processed / data is processed
More help here:
7b answer
- To store instructions/data that is frequently used / previously used / next to be used
- Data does not need to be fetched from RAM
- Speeds up access
More help here - Cache memory explained
7c answer
E.g.
Memory;
Memory;
- Smaller in size
- Faster access
- Larger capacity
- More durable
- Costs less per byte/kb etc
- be smaller
- be more mobile/portable
- have similar capacity
8ai answer
- (Part of the instruction which) specifies the operation to be carried out
- e.g. 00001000 = add to timer/00000100 = subtract from timer
More help here - Opcode explained
8aii answer
- (Part of the instruction which) supplies the data/ address/value needed for an operation
- e.g. the number to be added/subtracted from the timer / numerical example from the table (00010100 or 00000001)
More help here - Operand explained
8b answer
8c answer
- Instructions and data are fetched at different points of the fetch execute cycle
- Instructions and data are kept in separate parts of the memory (by the operating system)
9a answer
e.g.
- record log on / log off times
- remote access / view users’ screens
- audit printing
- keylogging
- monitor internet usage / downloads
- monitoring emails / files sent / copied
- inspect files in users’ areas
9b answer
IP addresses can be changed / are allocated as needed
MAC addresses can’t be changed / every device has a fixed MC address
IP(v4) addresses are 4 bytes long
MAC addresses are 6 bytes long
IP(v4) addresses are normally written in denary
MAC addresses are normally written in Hex
IP addresses are configured by software
MAC addresses are configured in hardware
IP addresses are used for routing across a WAN/internet
MAC addresses are only used within the LAN
[marks in pairs, maximum 2 pairs]
More help here - IP address
MAC addresses can’t be changed / every device has a fixed MC address
IP(v4) addresses are 4 bytes long
MAC addresses are 6 bytes long
IP(v4) addresses are normally written in denary
MAC addresses are normally written in Hex
IP addresses are configured by software
MAC addresses are configured in hardware
IP addresses are used for routing across a WAN/internet
MAC addresses are only used within the LAN
[marks in pairs, maximum 2 pairs]
More help here - IP address
9c answer
- Redundant components/hardware/capacity (servers/disks/routers etc) is built into the network
- If there is a failure, network automatically switches to use the spare capacity
- Allows the bank to continue to operate / avoids network downtime
- avoiding loss of income /customer dissatisfaction/ loss of records / other example related to the bank
More help here - failover
10a answer
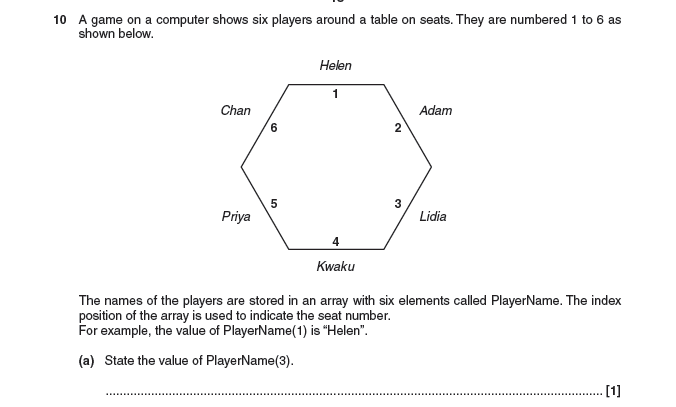
Lidia
10b answer
- Program finds there is no position 7 in the array / array index out of bounds
- An error will occur / an error message would be displayed / program will crash
10c answer
Example:
INPUT Num
For i = 1 to Num
Temp = PlayerName(6)
PlayerName(6) = PlayerName(5)
PlayerName(5) = PlayerName(4)
PlayerName(4) = PlayerName(3)
PlayerName(3) = PlayerName(2)
PlayerName(2) = PlayerName(1)
PlayerName(1) = Temp
Next i
Award marks for:
INPUT Num
For i = 1 to Num
Temp = PlayerName(6)
PlayerName(6) = PlayerName(5)
PlayerName(5) = PlayerName(4)
PlayerName(4) = PlayerName(3)
PlayerName(3) = PlayerName(2)
PlayerName(2) = PlayerName(1)
PlayerName(1) = Temp
Next i
Award marks for:
- Input the number of places to move (e.g. Num)
- Use of temporary variable(s) or second array to avoid overwriting values in the array
- Sensible use of a loop
- ... with correct end condition
- Correctly deals with moving from position 1 (e.g. 1 + Num)
- Correctly deals with moving from position 6 (e.g. Num )
Loading OCR 2015