Solid state disc drive
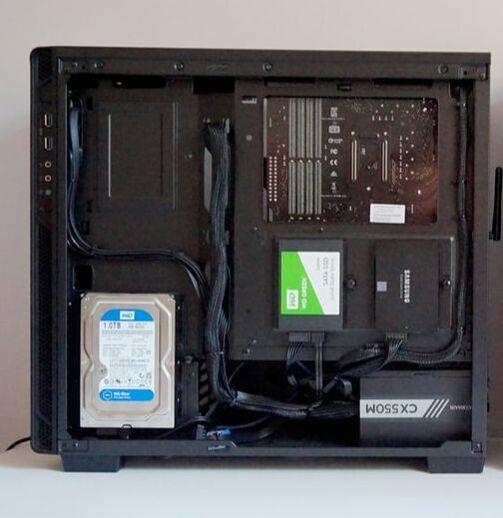
Computers have a (secondary) storage device called a disk drive, It is where all your apps are stored. There are currently two types of storage device, the magnetic hard disk drive and the solid state disk drive.
How does a solid state drive work?
- When you take the cover off a solid state drive/USB memory stick, you will see NAND flash memory cells (as below)
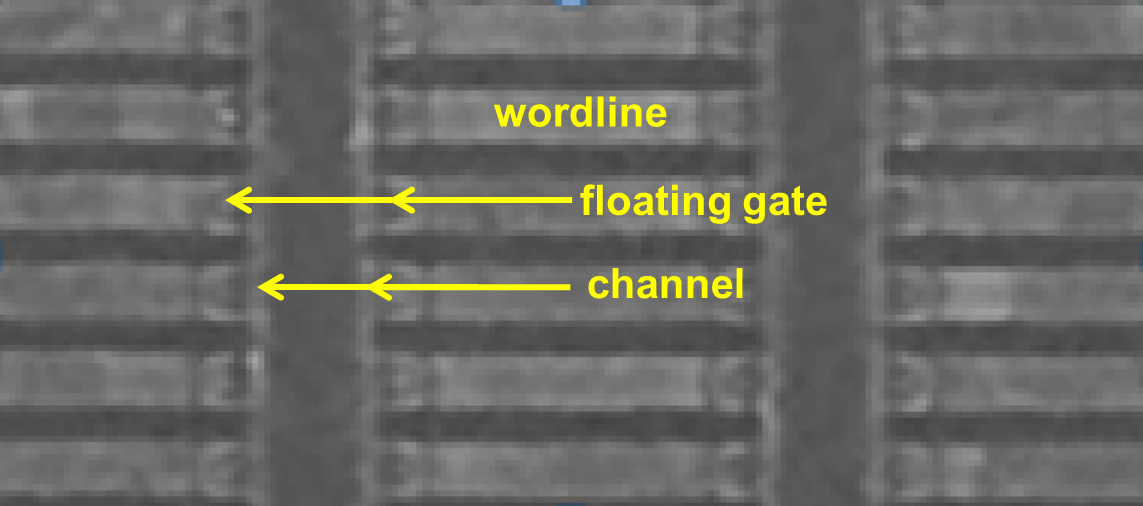
- Inside NAND flash memory cells are billions of "Floating gate transistors" arranged as a grid
- Floating gate transistors (are a bit like cups that) trap electrons in a "pool"
- When opening data from a SSD, if one floating gate transistor contains electrons, the computer reads it as a "zero". If another floating gate transistor is empty of electrons, the computer read it as a "one"
- When saving data to a SSD, an electrical charge (from the computer) is used to create binary string which is sent to the SSD. A charge causes electrons to move between two pools
- To erase data from a SSD, a high voltage removes electrons from the pools.
NAND flash memory magnified
Examples of solid state media
Loading Solid state drive