1A(i) Answer
Any two of:
Edexcel computer science steve cushing - p.188
- Large storage capacity
- Non-volatile
- Fast data access speed
- Portable
Edexcel computer science steve cushing - p.188
1a(ii) answer
1b(i) answer
Any one of:
Edexcel computer science steve cushing - p.136
- To reduce download time/increase transfer speed
- To reduce amount of storage space required
Edexcel computer science steve cushing - p.136
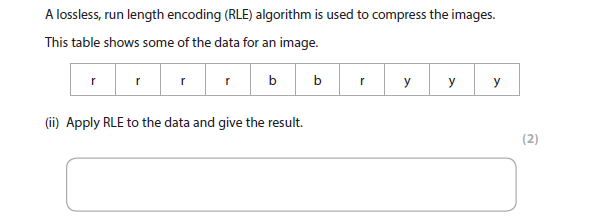
1b(ii) answer
Any one of:
More help here - RLE
Edexcel computer science steve cushing - p.136
- R4B2R1Y3
- R4B2RY3
- 4R2BR3Y
- 4R2B1R3Y
More help here - RLE
Edexcel computer science steve cushing - p.136
1c answer
Any two of:
More help here - Lossy
Edexcel computer science steve cushing - p.140
- Not all pixels are recorded
- Quality/detail reduced
- Only suitable when images have lots of the same pixels
- Cannot reproduce original using the lossy data
More help here - Lossy
Edexcel computer science steve cushing - p.140
1d(i) answer
Each character is shifted in the alphabet (1) by a fixed number of positions (1)
More help here - Caesar cipher
Edexcel computer science steve cushing - p.146
More help here - Caesar cipher
Edexcel computer science steve cushing - p.146
1d(ii) answer
E becomes A (1), A becomes W (1)
LAW
LAW
1e answer
Any two of:
More help here - Bit depth
Edexcel computer science steve cushing - p.126
- Images stored in (an array of) pixels
- Number of pixels determines the quality of the image
- The number of bits in each pixel determines how many colours/shades
- Can be encoded to reduce the file size
More help here - Bit depth
Edexcel computer science steve cushing - p.126
1f(i) answer
5mb x 2000 = 10,000mb
= 10gb
Answer = C or 16GB
More help here - Conversion
Edexcel computer science steve cushing - p.135
= 10gb
Answer = C or 16GB
More help here - Conversion
Edexcel computer science steve cushing - p.135
1f(ii) answer
Number of bits = 5 x 2000 x 1024 x 1024 (1)
Time = Number of bits/transfer rate
OR
Time = Number of bits/bps (1)
More help here - Transfer rate
Edexcel computer science steve cushing - p.144
Time = Number of bits/transfer rate
OR
Time = Number of bits/bps (1)
More help here - Transfer rate
Edexcel computer science steve cushing - p.144
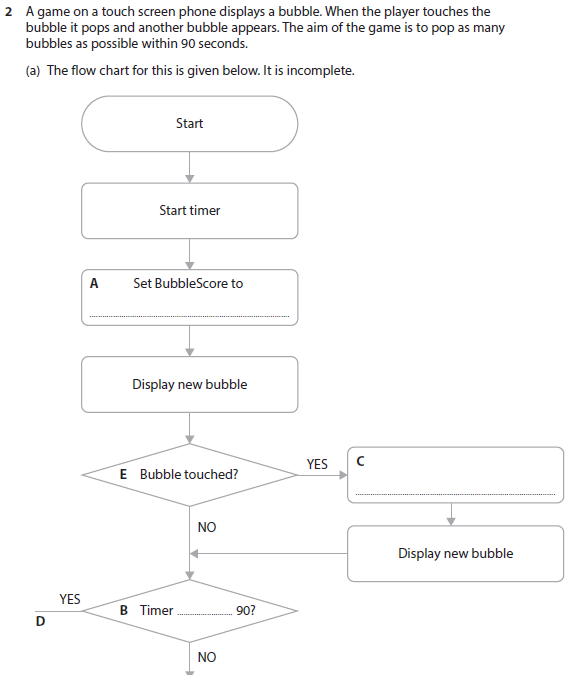
2a(vi) answer
2b(i) answer
A named (1) storage/memory location (1)
More help here - Variable
Edexcel computer science steve cushing - p.102
More help here - Variable
Edexcel computer science steve cushing - p.102
2b(ii) answer
Integer (1)
Any one of:
More help here - Data types
Edexcel computer science steve cushing - p.59, 65
Any one of:
- Type integer allows only whole numbers (1)
- Integer data type allows calculations (1)
More help here - Data types
Edexcel computer science steve cushing - p.59, 65
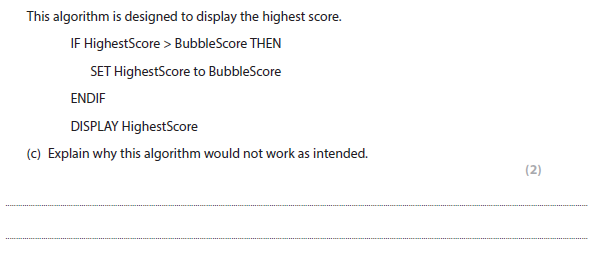
2c answer
Any one of:
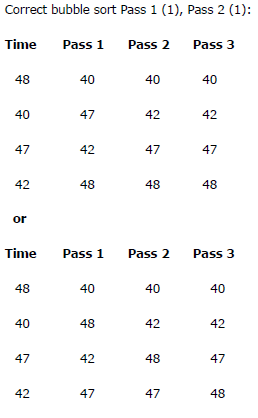
Incorrect comparison (1) should be < (1)
OR
Replaces HighestScore with BubbleScore if BubbleScore is less than HighestScore (1)
should be greater than (1)
Incorrect comparison (1) should be < (1)
OR
Replaces HighestScore with BubbleScore if BubbleScore is less than HighestScore (1)
should be greater than (1)
2d(i) answer
Because all the items in the list have the same data type (1)
It is more efficient to access and process data (1)
More help here - Array
Edexcel computer science steve cushing - p.69
It is more efficient to access and process data (1)
More help here - Array
Edexcel computer science steve cushing - p.69
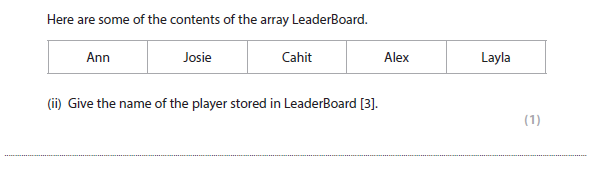
2d(ii) answer
Alex
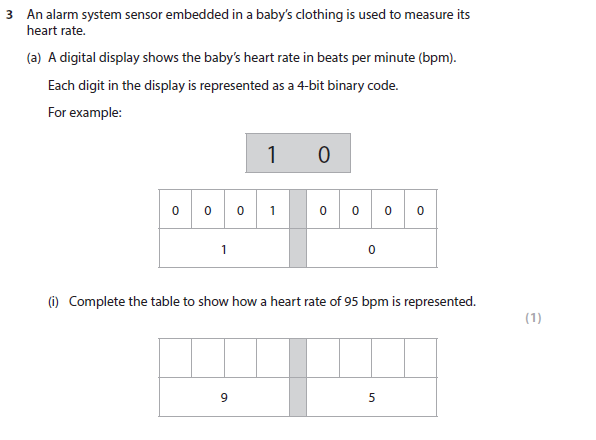
3a(i) answer
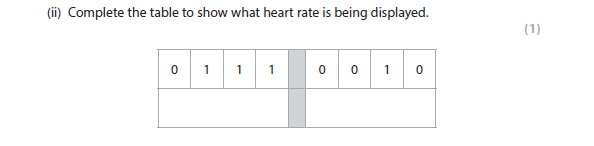
3a(ii) answer
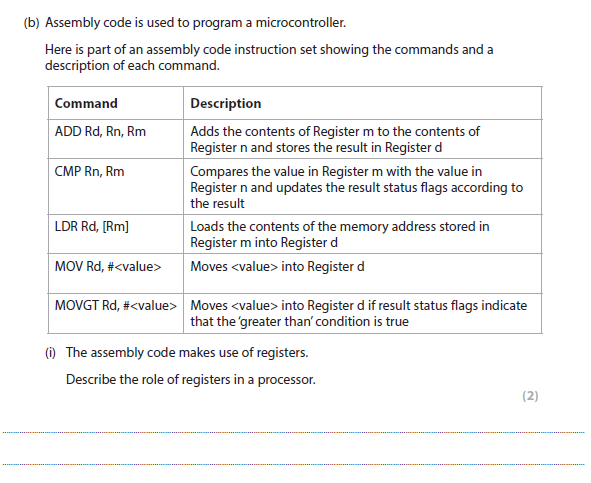
3b(i) answer
Provides small amount of storage (in the processor)(1)
holds an instruction/memory address/data value (1)
More help here - CPU
Edexcel computer science steve cushing - p.203
holds an instruction/memory address/data value (1)
More help here - CPU
Edexcel computer science steve cushing - p.203
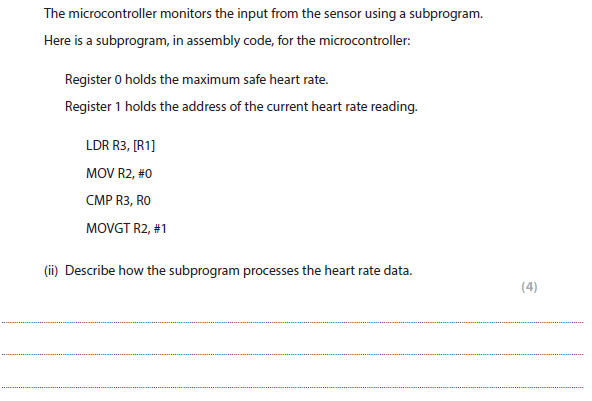
3b(ii) answer
Any four of:
More help here - Assembly code
- Puts the heart rate into register 3 (1)
- Sets value/flag/register 2 to 0 (1)
- Compares heart rate with maximum safe level (1)
- If heart rate too high sets value/flag/register 2 to 1 (1)
- Returns a value 0 if heart rate is within
- safe region or 1 if heart rate is too high (1)
More help here - Assembly code
3b(iii) answer
0111 0011
3c(i) answer
3c(ii) answer
The more lines/wires/bits the address bus has (1) the more memory locations can be uniquely identified (1)
3c(iii) answer
3d(i) answer
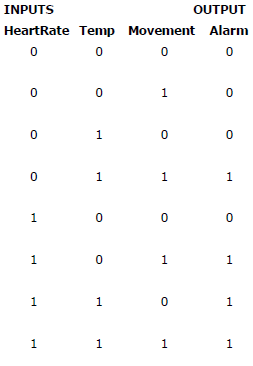
Alarm = (Heart Rate AND Temperature)
OR
(Heart Rate AND Movement)
OR
(Temperature AND Movement)
OR
(Heart Rate AND Movement)
OR
(Temperature AND Movement)
4a answer
Correct calculation using variables (1)
For example:
Use of variable for result (1)
For example:
For example:
- DIVIDE TotalTime by NumberLaps (1)
- TotalTime/NumberLaps (1)
Use of variable for result (1)
For example:
- SET AverageTime (1)
- STORE AverageTime (1)
4b(i) answer
Any one suitable benefit with expansion:
More help here - Sub program / user defined function
Edexcel computer science steve cushing - p.203
- makes code easier to understand (1) because it uses user-friendly language (1)
- quicker to write subprogram (1) because standard routines (wizards) available (1) easier to modify (maintain)(1) because
- of meaningful variable names/ clarifying comments (1)
- machine independent/can run on a variety of hardware (1) because program can be compiled as required for particular computers
More help here - Sub program / user defined function
Edexcel computer science steve cushing - p.203
4b(ii) answer
Any one of:
More help here - Sub program / user defined function
Edexcel computer science steve cushing - p.203
- Can be reused
- Improves readability of program
- Easier to debug a small chunk of code rather than a whole program
- Make it easier to divide the task up between a number of programmers
More help here - Sub program / user defined function
Edexcel computer science steve cushing - p.203
4c answer
4d(i) answer
SELECT Forename, EmailAddress
FROM Member
WHERE RenewalMonth = 'September';
1 mark for correct two fields in SELECT clause
1 mark for FROM clause
1 mark for correct WHERE clause
More help here - SQL
Edexcel computer science steve cushing - p.156-160
FROM Member
WHERE RenewalMonth = 'September';
1 mark for correct two fields in SELECT clause
1 mark for FROM clause
1 mark for correct WHERE clause
More help here - SQL
Edexcel computer science steve cushing - p.156-160
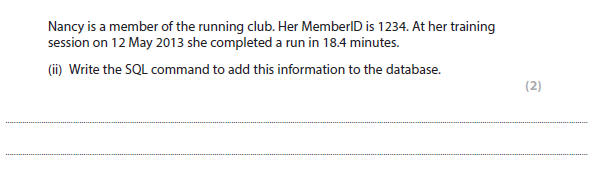
4d(ii) answer
INSERT into Run (1234, 2013-05-12, 18.4)
1 mark for INSERT INTO Run
1 mark for correct statement including values
More help here - SQL
Edexcel computer science steve cushing - p.156-160
1 mark for INSERT INTO Run
1 mark for correct statement including values
More help here - SQL
Edexcel computer science steve cushing - p.156-160
4d(iii) answer
SELECT DateOfRun,Time
FROM Run
WHERE MemberId = 0012
ORDER BY Time
More help here - SQL
Edexcel computer science steve cushing - p.156-160
FROM Run
WHERE MemberId = 0012
ORDER BY Time
More help here - SQL
Edexcel computer science steve cushing - p.156-160
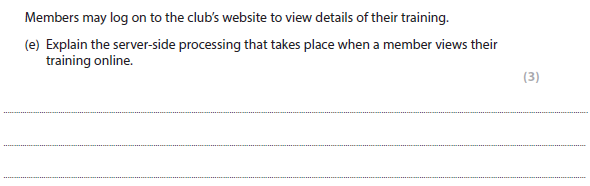
4e answer
Request from club member handled by a script server side (1). Server accepts request and retrieves training data from database (1) Constructs web page to display results of search (1) and sends to client computer (1)
More help here - Client Server
Edexcel computer science steve cushing - p.
More help here - Client Server
Edexcel computer science steve cushing - p.
5b answer
Indicative content:
Security: a private WAN is more secure because the railway company is the only user; a VPN uses a public network such as the internet, therefore is more vulnerable to attack. Encryption required.
Performance, reliability and control: Network/bandwidth solely for the railway company’s use
Control: as sole user of the private WAN the railway company has complete control over how it is set up and run; if using a VPN the railway company will have far less control since the network service provider will need to balance the needs of all users of the network.
Cost: the railway company must bear all the cost of setting up and running the private WAN; the VPN uses a public network so the costs are spread between many users.
Expertise: setting up and running a private WAN requires technical/managerial expertise which the railway company may not have; using a VPN on a public network outsources these activities to a service provider.
How to get full marks - A balanced response with sound and relevant points from more than one of the above examples Response includes a recommendation that is fully justified with regard to the rail company. Response is clearly structured, with sound control of expression and meaning. Spelling and punctuation are mostly accurate, with some errors.
Edexcel computer science steve cushing - p.213
Security: a private WAN is more secure because the railway company is the only user; a VPN uses a public network such as the internet, therefore is more vulnerable to attack. Encryption required.
Performance, reliability and control: Network/bandwidth solely for the railway company’s use
Control: as sole user of the private WAN the railway company has complete control over how it is set up and run; if using a VPN the railway company will have far less control since the network service provider will need to balance the needs of all users of the network.
Cost: the railway company must bear all the cost of setting up and running the private WAN; the VPN uses a public network so the costs are spread between many users.
Expertise: setting up and running a private WAN requires technical/managerial expertise which the railway company may not have; using a VPN on a public network outsources these activities to a service provider.
How to get full marks - A balanced response with sound and relevant points from more than one of the above examples Response includes a recommendation that is fully justified with regard to the rail company. Response is clearly structured, with sound control of expression and meaning. Spelling and punctuation are mostly accurate, with some errors.
Edexcel computer science steve cushing - p.213
5c answer
RECEIVE StartStation from (STRING) CARD
READER
SET Index TO 0
SET Found TO false
WHILE Found = false DO
IF ListOfStations.Station[Index] =
StartStation THEN
SET Found TO True
ELSE
SET Index TO Index + 1
END IF
END WHILE
IF ListOfStations.Distance[Index] < 5 THEN
SET CostOfJourney TO 2.50
ELSE
IF ListOfStations.Distance[Index] >12
THEN
SET CostOfJourney TO 4.15
ELSE
SET CostOfJourney TO 3.25
END IF
END IF
IF (Time >10.00 AND Time <17.00) OR (Day =
Saturday OR Day = Sunday) THEN
SET Cost TO Cost*0.9
END IF
SEND [“The cost of your journey is £”,
CostOfJourney, “Thank you for travelling on our
railway.”] TO DISPLAY
READER
SET Index TO 0
SET Found TO false
WHILE Found = false DO
IF ListOfStations.Station[Index] =
StartStation THEN
SET Found TO True
ELSE
SET Index TO Index + 1
END IF
END WHILE
IF ListOfStations.Distance[Index] < 5 THEN
SET CostOfJourney TO 2.50
ELSE
IF ListOfStations.Distance[Index] >12
THEN
SET CostOfJourney TO 4.15
ELSE
SET CostOfJourney TO 3.25
END IF
END IF
IF (Time >10.00 AND Time <17.00) OR (Day =
Saturday OR Day = Sunday) THEN
SET Cost TO Cost*0.9
END IF
SEND [“The cost of your journey is £”,
CostOfJourney, “Thank you for travelling on our
railway.”] TO DISPLAY
Loading Sample assessment 1