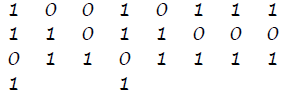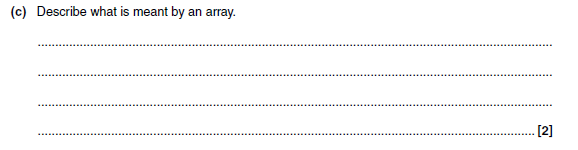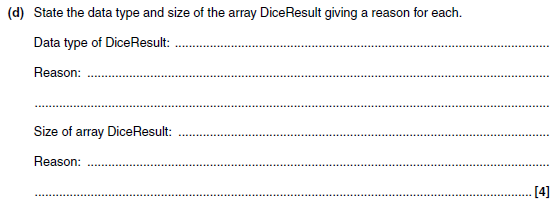1A Answer
To carry out the processing on the computer/To (fetch and) execute instructions'
More help here - Fetch decode execute explained
More help here - Fetch decode execute explained
1B answer
3MHz. Two from
More help here - Clock speed explained
- 3MHz is the clock speed / how fast the processor is
- Indicates how many instructions may be processed in each second
- Indicates how many clock cycles per second
More help here - Clock speed explained
1B answer
Quad core
More help here - Quad core explained
- The computer has 4 cores...
- …which are independent processors within the CPU ..
- ... working simultaneously / can perform multiple tasks
More help here - Quad core explained
2a answer
Two from:
- To share the printer
- To share the internet connection
- To share files
- To communicate with each other eg by email
2b answer
- Bus “line” shown
- Terminators shown at each end of bus
- 3 computers attached to bus
- Printer attached to bus or to a computer
- Internet connection connected to Router or to a computer
- Network adapters are needed on each computer
- Router needed to share the Internet connection
- Cables needed to connect the different devices
More help here - Bus network
3a answer
5a answer
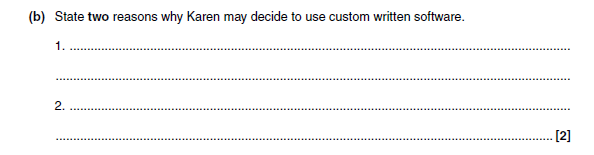
Software created especially for a user/the restaurant
5b answer
Two from:
- Appropriate software may not exist
- Existing software may not do exactly what restaurant wants
- Existing software may not be compatible with restaurant’s hardware
- Existing software may contain additional features (more complex and expensive)
5c answer
Points to be made include:
- Open source – licence-free, the restaurant will make the software and its source code available for others to use/improve.
- Financial implications include: no need to pay for license, can reuse/adapt free open source software which is similar BUT loss of development costs/software will be available to competitors
- Quality implications include: large community of open source developers can see and comment on code or can be consulted/ software has to conform to certain standards to be released under public licence BUT open source code is used as is, with no guarantees,
- Ethical implications include: Open source encourages “open culture” values - free sharing, collaboration BUT restaurant is a business trying to make a profit.
6 answer
Input device:
More help here -
- Joystick
- To control the CCTV cameras
- … to zoom/tilt/pan
- … as they allow precise movements (in 2 axis)
- Keyboard
- To type commands into the system…
- … to perform complex control tasks
- Key presses can be used to control the cameras
More help here -
6 answer
Output device:
- Monitor/Array of monitors
- Show the output of cameras
- Showing multiple cameras at a time
- Printer
- To print hard copy images from the recordings
- eg to be used as evidence
6 answer
Storage device
- hard disk drive with large capacity
- to record feed from all cameras…
- … simultaneously
- … allows direct access to any part of the recording
- rewritable large optical drive/removable flash storage
- to save recordings (eg for a given day)
- for archiving purposes
7a answer
- A real world object
- ... about which data is stored in a database
- Corresponds to tables in the database
7bi answer
- Primary Key: PupilNumber
7bi answer
- It is a unique identifier
- Two pupils cannot have the same PupilNumber...
- ... but they can have the same surname, firstname or ClassCode
More help here - Primary key
7c answer
- ClassCode is used here as a foreign key
- To link CLASS and PUPIL
- Using the ClassCode, all the class details can be retrieved from the Class table
- ... otherwise the class details will have to be rewritten everytime/to avoid data redundancy
More help here - Foreign key
8a answer
- An error in the rules/grammar of the language
- Any suitable example
More help here - Syntax errors explained
8B answer
- Error messages/translator diagnostics
- Produced when translating/by the compiler
- ... or on the fly while writing code
- Attempts to tell you what the error is
- And indicate where the error is/line numbers/underlines
- Editor...
- ... allows you to enter the corrected code
More help here - Python idle
9 answer
Points may include:
- Hardware: Computers faster & more capable of high speed Internet access – allows video and voice communication; large server farms and cheaper storage enables the infrastructure behind large social networking websites; convergence of computers with other digital technology (eg phones, television sets) allows continuity of networking over several formats.
- Software: Open standards and increased use of server side software (eg php) allow social networking sites to operate across all platforms. Open protocols allow several clients to use the same services or allow software to be written to allow different services to sync with each other; coexist. Software increasingly easier to use and easily adopted by younger generation.
10a answer
- Each character is given a numeric code
- Including symbols, digits, upper and lower case
- This code is then stored in binary
- Each character takes 1 byte
- Text is stored as a series of bytes (1 per character)
- Some codes are reserved for control characters (eg TAB, Carriage Return)
More help here - Ascii explained
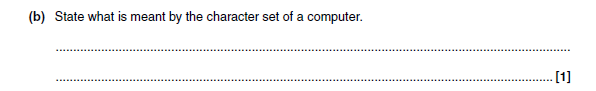
10b answer
All the characters which are recognised/can be represented by the computer system
10c answer
- Unicode has a much larger character set
- ... and can represent many more characters/characters from all alphabets
- Because unicode uses 16 bits...
- ... and ASCII uses fewer/7/8 bits
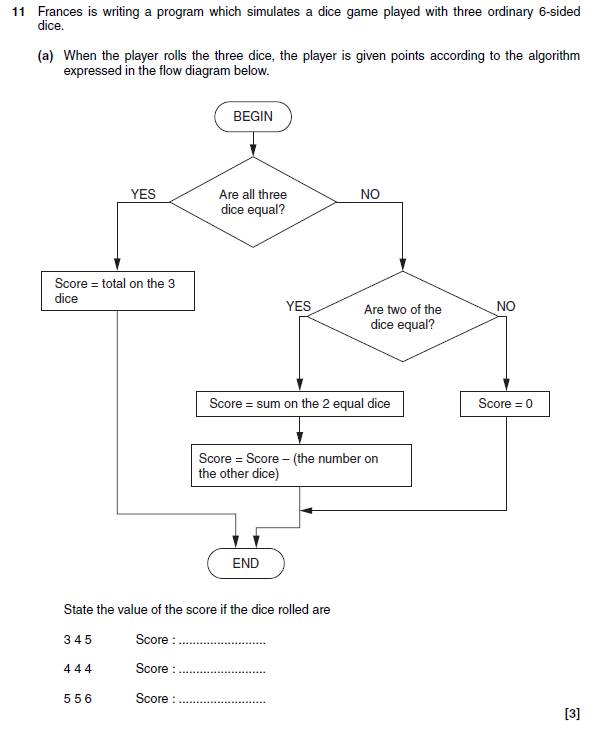
11 answer
- 0
- 12
- 4
11b answer
Test data : 1 1 3/1 1 4/1 1 5/1 1 6/2 2 5/2 2 6
Expected output: -1 -2 -3 -4 -1 -2
Award one mark for correct test data, and one mark for the correct corresponding outcome.
Expected output: -1 -2 -3 -4 -1 -2
Award one mark for correct test data, and one mark for the correct corresponding outcome.
11c answer
Two from:
-
- A data structure/collection of several variables
- Under one name
- Each individual variable is given an index
- by which it is referred within the array
-
11d answer
- Data type: Integer
- Reason: A dice roll is always a whole number (between 1 and 6)
- Size: 3
- one element is needed for each dice
11e answer
Example
BEGIN RollTheDice
i = 1
WHILE i <= 3
DiceRoll(i) = Random No
END WHILE
END
Award marks for:
BEGIN RollTheDice
i = 1
WHILE i <= 3
DiceRoll(i) = Random No
END WHILE
END
Award marks for:
- Using a loop
- i (or equivalent) initialised correctly
- correct end condition for loop/loops the required number of times
- Correct use of i (or equivalent) in DiceRoll(i)