1A Answer (AO1)
C Unsigned integers store more positive values
The only correct answer is C
A is not correct because unsigned integers are not more accurate
B is not correct because overflow errors can still occur with unsigned integers
D is not correct because the use of a parity bit is not relevant to the scenario.
More help here -
The only correct answer is C
A is not correct because unsigned integers are not more accurate
B is not correct because overflow errors can still occur with unsigned integers
D is not correct because the use of a parity bit is not relevant to the scenario.
More help here -
1B answer (AO2)
Award one mark for sight of either 1024 to the power of 4 OR x4
Award both marks for a correct expression including 10244 AND x4 (with nothing else)
e.g. 1024 to the power of 4 x 4
Accept for 10244 any equivalent showing understanding that 1 terabyte is 240 bytes
e.g.
● 1024 x 1024 x 1024 x 1024 (bytes)
● 2 to the power of 10 x 2 to the power of 10 x 2 to the power of 10 x 2 to the power of 10 (bytes)
● 1,099,511,627,776 (bytes)
Award both marks for 4,398,046,511,104 (bytes).
More help here -
Award both marks for a correct expression including 10244 AND x4 (with nothing else)
e.g. 1024 to the power of 4 x 4
Accept for 10244 any equivalent showing understanding that 1 terabyte is 240 bytes
e.g.
● 1024 x 1024 x 1024 x 1024 (bytes)
● 2 to the power of 10 x 2 to the power of 10 x 2 to the power of 10 x 2 to the power of 10 (bytes)
● 1,099,511,627,776 (bytes)
Award both marks for 4,398,046,511,104 (bytes).
More help here -
1C answer (AO2)
Award both marks for.
● P AND (T OR S)
● (P AND T) OR (P AND S)
Award one mark for:
● (P AND T) OR S
● P AND T OR S
More help here -
● P AND (T OR S)
● (P AND T) OR (P AND S)
Award one mark for:
● (P AND T) OR S
● P AND T OR S
More help here -
1D answer (AO1)
One from :
● 68
● 82 – 14
● R – D
● 18 – 4
Plus
● 0100 0100
More help here -
● 68
● 82 – 14
● R – D
● 18 – 4
Plus
● 0100 0100
More help here -
1e answer (AO1)
To prevent unauthorised reading/use/analysis/understanding (1)
of sensitive/payment/personal/customer data (1)
More help here -
of sensitive/payment/personal/customer data (1)
More help here -
2a answer (AO2)
A linked description such as:
A record for each guest (1)
that uses attributes for guest characteristics (1)
More help here -
A record for each guest (1)
that uses attributes for guest characteristics (1)
More help here -
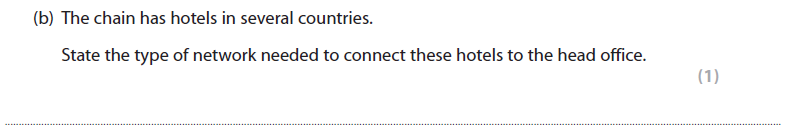
2b answer (AO1)
WAN / Wide Area Network
More help here -
More help here -
2c answer (AO2)
Indicative content:
● Cost - can be cheaper than hardware / can cost a lot for large amounts of data
● Space - likely to get more than on physical drives
● Scalability
● Trust / Control
● Physical security
● Access (read/write) speeds and impact on uses/applications
● Shared storage vs dedicated
● Often belongs to a third party
● Bandwidth limitation
● Data vulnerability due to unknown provider
● Access from any Internet devices
More help here -
● Cost - can be cheaper than hardware / can cost a lot for large amounts of data
● Space - likely to get more than on physical drives
● Scalability
● Trust / Control
● Physical security
● Access (read/write) speeds and impact on uses/applications
● Shared storage vs dedicated
● Often belongs to a third party
● Bandwidth limitation
● Data vulnerability due to unknown provider
● Access from any Internet devices
More help here -
2d answer (AO1)
B – TCP/IP
The only correct answer is B
A is not correct because HTML is not a protocol
C is not correct because an ISP is not a protocol
D is not correct because a URL is not a protocol
More help here -
The only correct answer is B
A is not correct because HTML is not a protocol
C is not correct because an ISP is not a protocol
D is not correct because a URL is not a protocol
More help here -
2e answer (AO1)
A description to include two from:
● each node/device is connected to multiple other nodes/devices
● it is decentralised
● ensures data can still be routed to the destination address if one node fails
● self-configuring
More help here -
● each node/device is connected to multiple other nodes/devices
● it is decentralised
● ensures data can still be routed to the destination address if one node fails
● self-configuring
More help here -
3a answer (AO1)
A description to include three from:
● NAND (memory)
● If a row/column/set of transistors conduct current / are open/charged, then this represents a 1
● If row/column/set transistors do not conduct current / are closed/uncharged, then this represents a 0
● Arranged in a grid (columns/rows)
● At row/column intersections, two transistors (control gate and floating gate) create a ‘cell’
● By applying voltage to the control gate transistors
● Electrons flow onto the floating gate
● Creates a net positive charge that interrupts current flow
More help here -
● NAND (memory)
● If a row/column/set of transistors conduct current / are open/charged, then this represents a 1
● If row/column/set transistors do not conduct current / are closed/uncharged, then this represents a 0
● Arranged in a grid (columns/rows)
● At row/column intersections, two transistors (control gate and floating gate) create a ‘cell’
● By applying voltage to the control gate transistors
● Electrons flow onto the floating gate
● Creates a net positive charge that interrupts current flow
More help here -
3B answer (AO1)
Any two from:
● Repairing files
● Compression
● Defragmentation
● Back up
● Anti-virus / anti-spyware / anti-malware
● Firewall
● Managing application updates
● Format disks/drives
● System analysis tools
More help here -
● Repairing files
● Compression
● Defragmentation
● Back up
● Anti-virus / anti-spyware / anti-malware
● Firewall
● Managing application updates
● Format disks/drives
● System analysis tools
More help here -
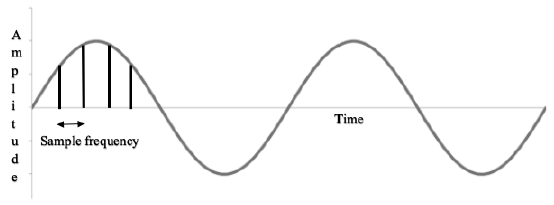
4aii answer (AO1)
The amplitude / original sound can be represented more accurately.
Accept:
● Better (sound) quality
● Higher fidelity
● Clearer (sound)
More help here -
Accept:
● Better (sound) quality
● Higher fidelity
● Clearer (sound)
More help here -
4B answer (AO1)
B – RAM
The only correct answer is B
A is not correct because the ALU does not hold a program
C is not correct because a hard drive does not hold a currently executing program
D is not correct because the control unit does not hold a program
More help here -
The only correct answer is B
A is not correct because the ALU does not hold a program
C is not correct because a hard drive does not hold a currently executing program
D is not correct because the control unit does not hold a program
More help here -
4c answer (AO2)
Total number of bits to transfer:
1 mark for 20 × 10242
1 mark for × 8
Speed in bits per second:
1 mark for 2 × 1000000
Numerator/Denominator:
1 mark for:
𝑏𝑖𝑡𝑠 𝑡𝑜 𝑡𝑟𝑎𝑛𝑠𝑓𝑒𝑟
____________________
𝑏𝑖𝑡𝑠 𝑝𝑒𝑟 𝑠𝑒𝑐𝑜𝑛𝑑
e.g:
𝟐𝟎 ×𝟏𝟎𝟐𝟒 ×𝟏𝟎𝟐𝟒 ×𝟖
_______________________
𝟐 ×𝟏𝟎𝟎𝟎𝟎𝟎𝟎
More help here -
1 mark for 20 × 10242
1 mark for × 8
Speed in bits per second:
1 mark for 2 × 1000000
Numerator/Denominator:
1 mark for:
𝑏𝑖𝑡𝑠 𝑡𝑜 𝑡𝑟𝑎𝑛𝑠𝑓𝑒𝑟
____________________
𝑏𝑖𝑡𝑠 𝑝𝑒𝑟 𝑠𝑒𝑐𝑜𝑛𝑑
e.g:
𝟐𝟎 ×𝟏𝟎𝟐𝟒 ×𝟏𝟎𝟐𝟒 ×𝟖
_______________________
𝟐 ×𝟏𝟎𝟎𝟎𝟎𝟎𝟎
More help here -
4d answer (AO2)
A description such as:
● Input from sensor (1)
● The input level is compared against pre-set values (1)
● Output to LED/speaker (1)
More help here -
● Input from sensor (1)
● The input level is compared against pre-set values (1)
● Output to LED/speaker (1)
More help here -
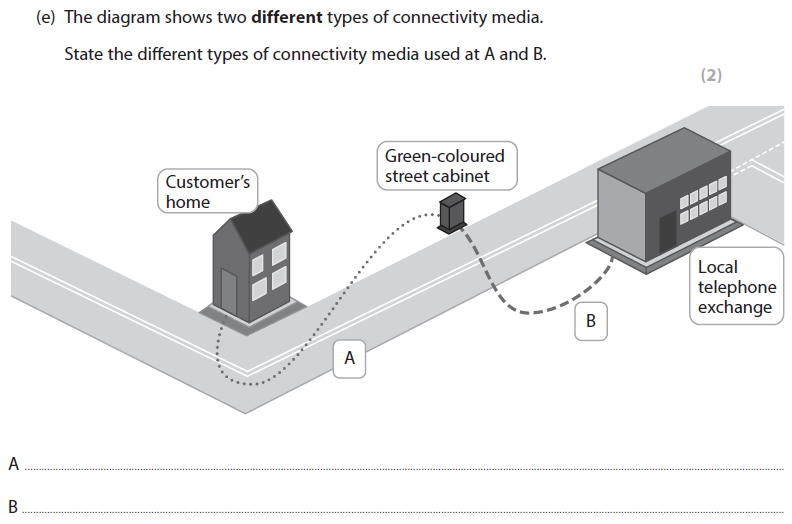
4e answer (AO2)
A. Copper cable
B. Fibre optic
More help here -
B. Fibre optic
More help here -
5a answer (AO1)
1101 1000
More help here -
More help here -
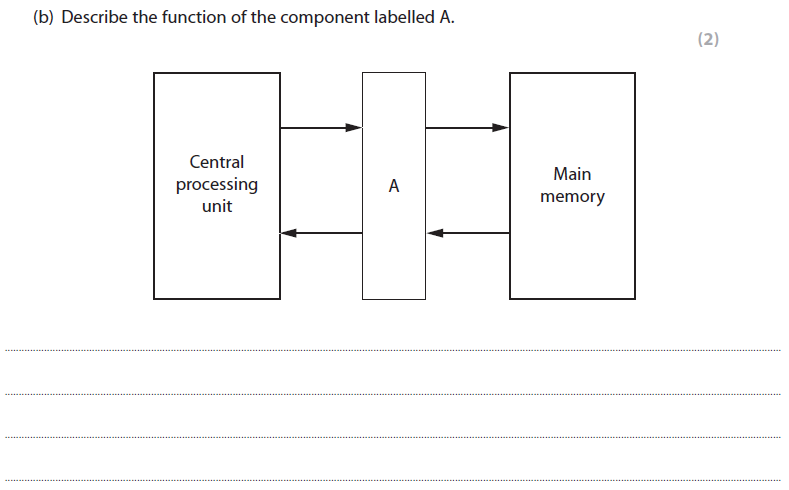
5b answer (AO2)
A description to include two from:
● (Cache) Stores regularly accessed instructions/data
● Reduces the need to access instructions/data from main memory
● Makes up for the difference in speed of the CPU and main memory
More help here -
● (Cache) Stores regularly accessed instructions/data
● Reduces the need to access instructions/data from main memory
● Makes up for the difference in speed of the CPU and main memory
More help here -
5c answer (AO2)
3D
More help here -
More help here -
5cii answer (AO1)
Hexadecimal is used as a short-hand for binary / uses fewer digits/characters (1)
so humans make fewer mistakes / find it easier to read/understand/remember/manipulate (1).
More help here -
so humans make fewer mistakes / find it easier to read/understand/remember/manipulate (1).
More help here -
5d answer (AO1)
A description to include four from:
The control unit increments the program counter (1)
The control unit sends a signal (1) along the control bus (1)
…to the memory/MAR (to tell it to send) (1)
…(the address of) the memory location (holding the instruction) (1) ...which is loaded onto the address bus (1)
...(and carried to RAM to tell it to) load the instruction/ contents of the memory location onto the data bus (1) ...along which it is carried to the MDR/MBR. (1)
More help here -
The control unit increments the program counter (1)
The control unit sends a signal (1) along the control bus (1)
…to the memory/MAR (to tell it to send) (1)
…(the address of) the memory location (holding the instruction) (1) ...which is loaded onto the address bus (1)
...(and carried to RAM to tell it to) load the instruction/ contents of the memory location onto the data bus (1) ...along which it is carried to the MDR/MBR. (1)
More help here -
5e answer (AO1)
It is not sorted
More help here -
More help here -
6a answer (AO2)
Award one mark for either:
Sight of: 1024 × 1024
OR
Sight of: divided by 64
Award both marks for correct expression, e.g.:
1024 × 1024
________________
64
More help here -
Sight of: 1024 × 1024
OR
Sight of: divided by 64
Award both marks for correct expression, e.g.:
1024 × 1024
________________
64
More help here -
6b answer (AO1)
A description such as:
The OS uses part of the secondary storage to act as part of main memory (1).
The OS moves programs that are not immediately needed out of main memory (1) and stores them in virtual memory / secondary storage (1) using paging (1)
Active programs are swapped into main memory (from virtual memory) (1).
More help here -
The OS uses part of the secondary storage to act as part of main memory (1).
The OS moves programs that are not immediately needed out of main memory (1) and stores them in virtual memory / secondary storage (1) using paging (1)
Active programs are swapped into main memory (from virtual memory) (1).
More help here -
6c answer (AO1)
Any one from:
● To check for bad programming practices
● To check for vulnerabilities in the programming language
● To check efficiency of code
More help here -
● To check for bad programming practices
● To check for vulnerabilities in the programming language
● To check efficiency of code
More help here -
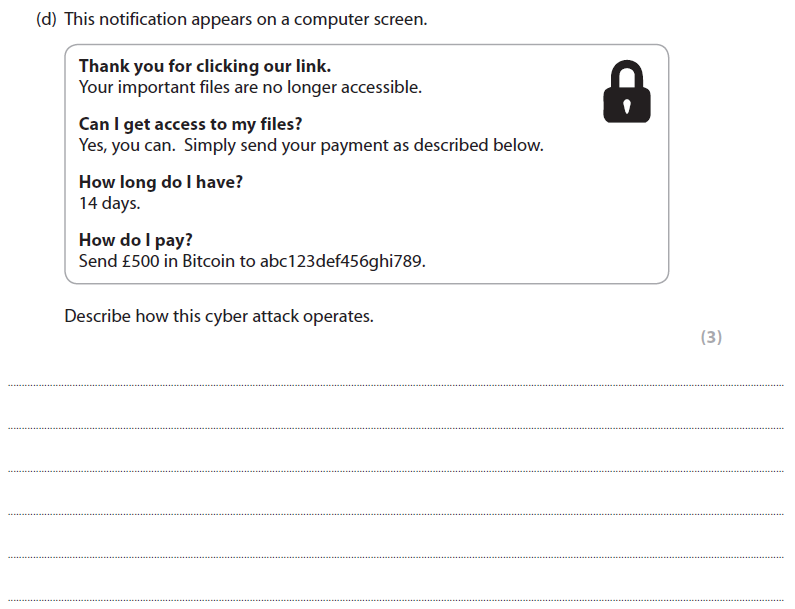
6d answer (AO2)
A description such as:
Ransomware / malicious attachment/download (1)
encrypts the user’s files (1).
To get the key/decrypt the files (1) … ...(the user must pay a ransom to the code writers / remove the malware)
More help here -
Ransomware / malicious attachment/download (1)
encrypts the user’s files (1).
To get the key/decrypt the files (1) … ...(the user must pay a ransom to the code writers / remove the malware)
More help here -
7a answer (AO1)
A linked description to include two from:
● Reads the packet header
● Takes the recipient's address
● Compares the (recipient’s) address to the addresses of all devices that are connected to it (which are stored in the router’s routing table)
● Forwards the packet / network traffic to its destination
● Using the quickest/most efficient route.
More help here -
● Reads the packet header
● Takes the recipient's address
● Compares the (recipient’s) address to the addresses of all devices that are connected to it (which are stored in the router’s routing table)
● Forwards the packet / network traffic to its destination
● Using the quickest/most efficient route.
More help here -
7b answer (AO1)
An explanation such as:
Changes in requirements / technology (1) mean that security can be improved/compromised (1)
OR
Changes in law/regulations (1) mean that requirements/technology must change (1)
Do not accept statements about unauthorised access / security that do not refer to changes in requirements / technology etc.
More help here -
Changes in requirements / technology (1) mean that security can be improved/compromised (1)
OR
Changes in law/regulations (1) mean that requirements/technology must change (1)
Do not accept statements about unauthorised access / security that do not refer to changes in requirements / technology etc.
More help here -
7c answer (AO1)
A description such as:
Each packet has a sequence number (added at the sending end) (1)
The packets are put back into (sequence) order (at the destination) (1).
More help here -
Each packet has a sequence number (added at the sending end) (1)
The packets are put back into (sequence) order (at the destination) (1).
More help here -
7d answer (AO1)
A response to include two linked points, such as:
● Some children may not have devices / can afford devices (1), so the school might have to provide them (1)
● Some students will have more advanced devices (1), thereby having different learning opportunities (1)
● Screen readers / facilitating programs (1) improve access for students with disabilities (1)
● Access may not be appropriate (1) for students from some religions / cultures (1)
● Opens opportunities for access to experts (1) thereby providing for individual needs (1)
More help here -
● Some children may not have devices / can afford devices (1), so the school might have to provide them (1)
● Some students will have more advanced devices (1), thereby having different learning opportunities (1)
● Screen readers / facilitating programs (1) improve access for students with disabilities (1)
● Access may not be appropriate (1) for students from some religions / cultures (1)
● Opens opportunities for access to experts (1) thereby providing for individual needs (1)
More help here -
Assessment Objectives occurrences in this exam
AO1 = 20 (Demonstrate knowledge and understanding of the key concepts and principles of computer science)
AO2 = 13 (Apply knowledge and understanding of key concepts and principles of computer science)
AO3 = 0 (Analyse problems in computational terms:
●to make reasoned judgements
●to design, program, evaluate and refine solutions.)
AO2 = 13 (Apply knowledge and understanding of key concepts and principles of computer science)
AO3 = 0 (Analyse problems in computational terms:
●to make reasoned judgements
●to design, program, evaluate and refine solutions.)